g = 2.855993321445266 .... - how to find pi to the number of graceli.
Number of graceli = g.
With the number of graceli becomes a relationship between geometry [pi], as algebra and calculus.
Because the number of graceli is a derivation of the number itself. And become part of number theory.
Graceli number theory.
Number of graceli. = G = 2.855993321445266 ................... * 1.1 = 3.141592653589793 ...................
It is an irrational number, transcendental, repeated sequences, and an infinitesimal number.
Pi divided by 1.1.
g = 2.855993321445266 ................... * 1.1 = pi = 3.141592653589793 .................. .
By nature is a sequential number and also an infinitesimal.
Note. For this number can be confirmed in sequential homes through nth pi, through spin, using the geometry calculation, algebra, trigonometry, derivatives, and various other branches.
Unlike the Euler number and the value of pi, this is fundamentally sequential infinitesimal.
The number of graceli besides being nine tenth of pi.
It is a sequence of repeated numbers.
It is its own derivative.
It is a transcendent irrational infinitesimal number.
How do you solve the multiple functions of infinitesimal graceli.
[P / p P [n]
G.
1- First solve the high progression exponent progression.
2- After solve the division of progression for each result of high progression progression.
After 3-held series of infinitesimal numbers solve for each series, each series high g.
The same is true if you use high g the logarithm of x / x.
[P / p P [n] [/ g].
G.
In other words, what we have is an infinitesimal system inside another infinitesimal system. Where for each first step we get a result, for every second step another result, and each third step another result.
In other words, what we have are many and varied results.
Derivation graceli.
Alone there have a system of curves variables and indeterminate [infinitesimal indeterminate].
But if it is raised the derivation we have are a different overlapping curves of the other, but with a few differences, that is what we have are forms of overlapping and variable curves.
[P / p P [n]
f [X].
[P / p P [n] / [g].
f [G].
with these functions have a totient function curves about curved, and an algebraic calculation.
Where each exponential result has been to divide the sequential number of graceli [g].
ix
g = cos [x] + i without [x].
ix
1 = [cos x - i sin x] * g
Theorem graceli between difference between hub proportionality and square.
The sum of the square two peccaries, when the sum of the two collared peccary is a prime, the hypotenuse is a transcendent irrational number.
And if high the sum of the other two sides of the same cube, the result never gives over the hypotenuse of these cubes.
Uniqueness graceli between fields and relativities and radiation.
The curved spacetime expanded differential pulses of electromagnetic waves and flows, ie, magnetism and electricity and electroweak.
As the intensity and inverse distance fields and radiation, and laser photons and produce deformations of space time, the dynamic inertia, and variations of expansion waves and pulses flows.
Φ = tG
ddf
EgG
i = 1
ddf 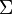
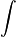 I = =D + v + fpo + dcd + TMNF. iiiG
I = =D + v + fpo + dcd + TMNF. iiiG
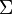
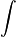 I = =D + v + fpo + dcd + TMNF. iiiG
I = =D + v + fpo + dcd + TMNF. iiiGD + v + fpo + dcd + TMNF.
Fpo = pulses and waves flows.
Deformation means and functional nature.
Deformations differential curve.
With this we have a unification between fields and relativities.
And in a broader scope of these variations have on physical media such as liquid, solid and gaseous modifying the structural and functional nature transformative thereof.
These variations happen all and in every tiny part as confirmed in the gas and its molecules, in the iron dilatation and mercury. Etc.
In other words, we have the general variations of micro and macro. Where does the cosmos and gravity.
And also with all fields.